Strategies to Avoid Repetitive Strain Injuries in Cycling
Introduction
Cycling is a fantastic way to boost fitness, enjoy the outdoors, and even improve mental health. However, as with any physical activity, cyclists are also at risk of certain injuries. One of the common issues faced by dedicated cyclists is repetitive strain injuries (RSIs). These injuries can affect performance and lead to prolonged recovery periods, thereby hindering one’s progression in the sport. Understanding and implementing strategies to avoid repetitive strain injuries are crucial for maintaining optimal cycling performance and enjoyment.
Repetitive strain injuries can severely impact your cycling performance metrics. Whether you’re recording increased cadence, monitoring power output, or keeping a keen eye on cycling speed, even minor discomfort can skew these metrics and reduce your overall biking efficiency. Furthermore, just as bike maintenance tips ensure your ride stays smooth, taking care of your body ensures that cycling remains enjoyable and injury-free.
Main Body
Training Techniques for Cyclists: The RSI Angle
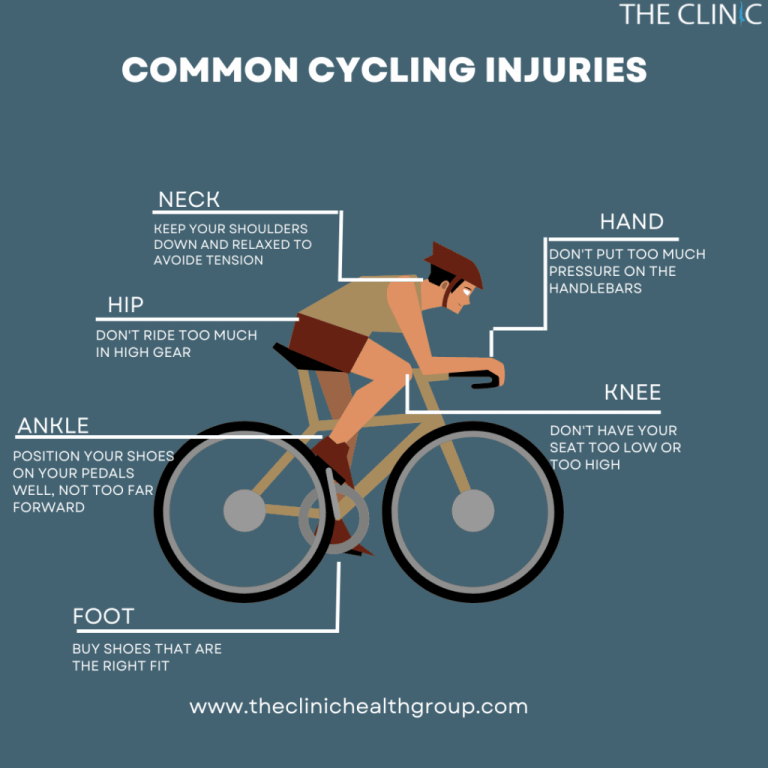
An essential aspect of effective cycling training involves understanding the nuances of ergonomics and posture correction. Ensuring that your riding position is optimized is key to preventing strain. Good posture includes a neutral spine, relaxed shoulders, and elbows slightly bent. You must routinely check that your bike’s setup minimizes the strain on your hands, wrists, and neck.
Break scheduling is another vital component. Continuous cycling without adequate rest can lead to overuse injuries. Implementing regular microbreaks not only aids muscle relaxation but boosts overall ride efficacy. During these breaks, stretching exercises focused on limbs and back can prevent stiffness and enhance performance consistency.
Best Nutrition Practices for Cyclists
Nutrition plays a role in muscle recovery and overall vitality. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods, like berries, nuts, and fatty fish, can help reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries. Staying hydrated is also vital because dehydration can exacerbate muscle fatigue and unintentional poor posture, increasing RSI risk.
Cycling Safety Tips and Ergonomics
Effective RSI prevention also involves considering safety equipment: ergonomic gadgets ensure better ride quality. For instance, choosing keyboard alternatives like ergonomic handlebars can distribute pressure more evenly across your palms. Mouse ergonomics, where applied to biking gear like handle grips, can enhance comfort and prevent nerve compression in the wrists.
While cycling, wrist support is crucial. Cyclists should ensure their wrists are not excessively flexed or extended. Adjustments can be made to handlebars to aid in this. Additionally, using voice recognition software for navigation reduces strain on hands, which frequently need to engage with devices mid-ride otherwise.
How to Choose the Right Cycling Gear
When choosing cycling gear, ergonomic equipment should be at the forefront. Helmets, gloves, and shoes that fit well and support correct alignment are key. Desk height adjustment may translate to seat and handlebar adjustments on your bike. Like in office ergonomics, proper setup ensures less strain and contributes to better performance.
Monitor positioning while cycling can be compared to ensuring your control console, like a cycling computer, is at the correct angle and easily visible without straining your neck.

Cycling Cadence and Performance Metrics
Cyclists often use devices to monitor cadence and other metrics essential for improving performance. However, frequently adjusting these devices can lead to RSIs. It’s beneficial to use mounts that hold devices firmly and comfortably at eye level. Regularly monitored VO2 max improvements indicate how well the body utilizes oxygen during extended rides, and doing these without strain helps performance.
Mental Resilience and Repetitive Strain Prevention
While less tangible, mental resilience plays a role in RSI prevention. Being aware of your limits and understanding the signals your body sends are crucial in avoiding strain. Mindful cycling helps you recognize early signs of discomfort, offering a chance to adjust before injuries develop.
Physical Therapy and Advanced Techniques
physical therapy is a proactive approach. Techniques taught by professionals can provide muscle relaxation techniques which aid in maintaining proper riding form. Hand exercises before and after rides can prevent the stiffening of muscles. Moreover, alternating activities to include varying intensity – akin to interval training for cycling – ensures muscles don’t continuously experience the same strain.
Activity Variation and Microbreaks
Variety in activity ensures that muscles don’t experience repetitive stress alone. Incorporating different cycling terrains, such as hills, flatlands, or even indoor cycling variations, offers a full-body workout and prevents overusing specific muscle groups. This principle is vital in activity variation.
Microbreaks, which involve short, frequent rests, can be crucial in managing fatigue and avoiding stress. These breaks can be spent performing simple stretches or massages to maintain muscle flexibility.
Data, Metrics, and Studies
Numerous studies highlight the importance of ergonomic adaptation to prevent injuries. Research shows that even minor adjustments in bike setups can reduce strain by a significant percentage, improving comfort and safeguarding long-term bike enjoyment. Utilizing power meters for performance tracking not only improves performance but helps detect any onset of strain that the body might be experiencing during cycling.

User Intent and Benefits
For those wondering how to improve endurance without risking repetitive strain, focusing on proper techniques is essential. Proper cycling techniques for beginners include paying attention to body alignment and gradually building ride duration. For those seeking to optimize their workouts, investing in ergonomic solutions prevents detours caused by injuries and keeps the focus squarely on performance gains.
The practical applications of these strategies ensure that cyclists remain active and free from injury, making every ride as enjoyable and effective as possible.
FAQs
Do repetitive strain injuries affect cycling speed?
Yes, RSIs can affect cycling speed by causing discomfort or pain, leading to inefficient riding and potentially slower speeds.
How often should I check my bike setup to prevent RSIs?
It’s advisable to check your bike setup every few months or if you notice any discomfort during your rides. A professional bike fitting can help ensure optimal ergonomics.
Are there specific stretches recommended for cyclists to prevent RSIs?
Yes, stretches focusing on the arms, shoulders, neck, and back can greatly alleviate pressure points and prevent stress injuries.
Can wrist support gear make a significant difference?
Absolutely. Wrist support gear can help maintain proper wrist alignment, reducing the pressure on nerves, and preventing strain or injury.
Is voice recognition software practical for all cyclists?
While it may not be practical for all situations, using voice recognition software for navigation aids can decrease hand usage, reducing risk of strain.
Conclusion
Repetitive strain injuries are a significant concern for cyclists, but with the right strategies, they can be effectively managed and prevented. Implementing proper ergonomics, scheduling breaks, ensuring proper bike setup, and varying activities are all pivotal in maintaining cycling health and performance. The result is a more enjoyable and injury-free cycling experience, empowering cyclists to push their limits while minimizing risks. Embrace these strategies and share your own experiences; your journey could inspire others to conquer the road fearlessly.