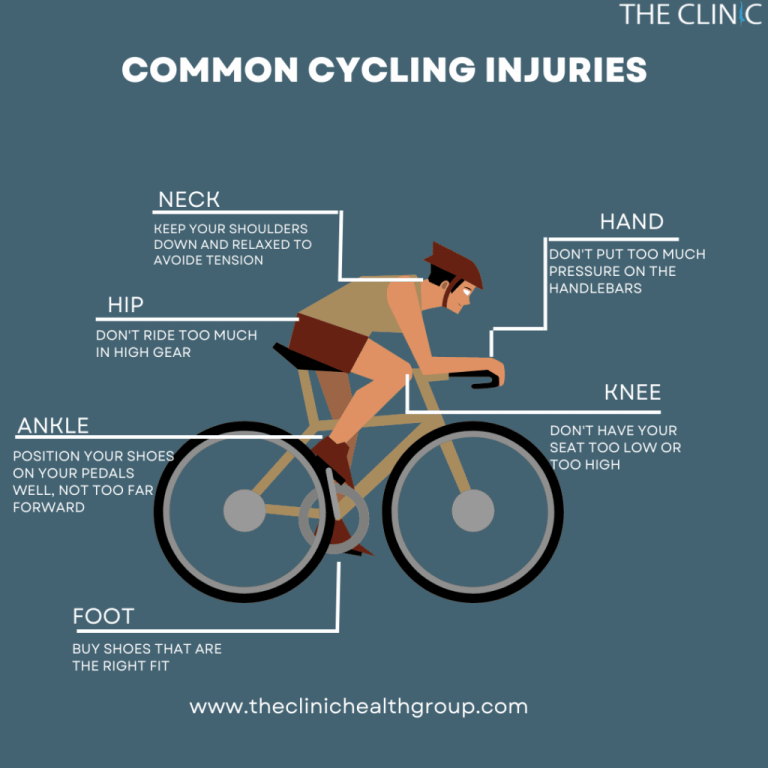
Injury Recovery for endurance cyclists: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Injuries can be a massive roadblock for endurance cyclists, but effective injury recovery is critical to getting back in the saddle. Injury recovery not only involves healing your body but also improving cycling performance metrics and ensuring bike maintenance is up to par. Endurance cycling pushes the body’s limits, requiring specific strategies for muscle regeneration and rehabilitation. This guide will explore essential techniques, including physical therapy, cycling biomechanics, strength training, and more, to help cyclists optimize their recovery journey.
Training Techniques for Cyclists
Endurance cycling demands a balanced approach to training:
interval training for Cycling
Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity cycling with rest or low-intensity riding, effectively boosting endurance and muscle strength. By incorporating these techniques, cyclists can manage muscle fatigue better, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Cycling Cadence and Performance Metrics
Understanding cycling cadence and tracking performance metrics with technology like power meters can provide insights into areas of improvement. This data-driven approach allows cyclists to personalize their training plans, aiding in faster recovery and enhanced performance.

Best Nutrition Practices for Cyclists
Nutrition is vital for injury recovery:
Recovery Nutrition
Proper recovery nutrition supports muscle regeneration and tissue repair. Cyclists should focus on carbohydrates for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and healthy fats for overall wellness. Including anti-inflammatory foods like berries and leafy greens can also help manage inflammation after long rides.
Hydration Strategies
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining performance and speeding up recovery. Hydration strategies should include water, electrolytes, and possibly carbohydrate-rich drinks during and after exercise to replenish what’s lost during rides.
Cycling Safety Tips
Preventing injuries is a crucial part of recovery:
Cycling Ergonomics
Proper cycling ergonomics helps to prevent wrist, shoulder, and back pain. Ensuring the bike is well-fitted to the rider can significantly reduce undue stress and improve posture.
Rest Periods and Overuse Injuries
Scheduling regular rest periods allows time for muscles to repair, reducing the risk of overuse injuries common in endurance cycling. A balanced training regime avoids excessive strain on any particular muscle group.
How to Choose the Right Cycling Gear
Optimal gear lessens the risk of injuries:
Compression Gear
Wearing compression gear during and after rides can improve blood circulation, reduce swelling, and enhance recovery. This gear is particularly beneficial in managing inflammation and promoting speedier muscle recovery.
Cycling Posture
Maintaining the correct cycling posture is vital for reducing the strain on your back and legs. Continuous training with poor posture can translate into chronic injuries.
Mental Resilience
Cycling is as much a mental challenge as it is physical:
Building Mental Resilience
Developing mental resilience helps cyclists keep motivated even after setbacks due to injuries. Techniques such as visualization, focus exercises, and goal setting can enhance training effectiveness and improve overall performance.
Power-based Training
Using a power meter helps cyclists focus on power output rather than just speed. This focus assists riders in maintaining consistent energy levels and avoiding unnecessary fatigue.
Advanced Recovery Techniques
Incorporate advanced methods for comprehensive recovery:
Massage Therapy
Regular massage therapy aids in muscle relaxation, reduces soreness, and speeds up the recovery process. It increases blood flow to the muscles, promoting healing and flexibility.
Cross-Training
cross-training by incorporating activities such as swimming or yoga can improve overall fitness without putting undue strain on cycling muscles. It contributes to a balanced fitness routine and aids in recovery.
Data, Metrics, and Studies
Scientific backing enhances understanding:
VO2 Max Improvements for Cyclists
Cyclists can improve their VO2 max, a crucial endurance metric, through consistent training and recovery practices. Studies show a direct correlation between enhanced VO2 max metrics and improved cycling performance.
Benefits of Using Power Meters for Performance Tracking
Utilizing a power meter helps in accurately monitoring progress. Research indicates cyclists implementing power-based training can significantly enhance performance and recovery by maintaining optimal energy output.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Essential to long-term success:
Orthopedic Assessment
An orthopedic assessment can pinpoint specific weaknesses or issues that may lead to injury. Such assessments can help create a tailored rehabilitation program that addresses individual needs effectively.
Sports Medicine
Working with sports medicine professionals can help cyclists develop personalized recovery plans that incorporate tailored exercises, stretches, and guidelines for returning to cycling.
User Intent and Benefits
Understanding user needs:
How to Improve Endurance
Cyclists looking to enhance endurance should focus on interval training, recovery nutrition, and adequate rest periods, leading to sustained performance improvements over time.
Cycling Techniques for Beginners
Beginners should prioritize learning proper cycling posture and ergonomics to prevent injuries and maximize comfort and efficiency.
Visual Content Suggestions
Boost engagement with relevant visuals:
– Consider an infographic illustrating ‘Cycling Cadence Improvement’.
– A diagram showing ‘Heart Rate Zones’ could enhance understanding of training techniques.
– Charts displaying ‘Training Progress’ over time, highlighting the impact of proper recovery methods, can be enlightening.

FAQs
1. Why is injury recovery important for endurance cyclists?
Injury recovery is crucial because it ensures the long-term well-being and performance of cyclists. It helps rebuild strength and prevent further injuries.
2. What are effective recovery nutrition strategies?
Focus on carbohydrates for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and anti-inflammatory foods. Stay hydrated with water and electrolytes.
3. How can cycling biomechanics prevent injuries?
Proper bike fitting and posture can help distribute the workload evenly, reducing the risk of strain and chronic injuries.
4. What role does mental resilience play in recovery?
Mental resilience keeps cyclists motivated through challenging recovery periods, helping maintain focus and commitment.
5. How can cross-training benefit cyclists?
Cross-training improves overall fitness by engaging different muscle groups, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Injury recovery is a multifaceted process, vital for the longevity and success of endurance cyclists. By implementing strategies like proper nutrition, regular stretching routines, mental resilience, and consulting with sports medicine professionals, cyclists can enhance their recovery process. Embrace these methods, share your experiences, and continue pushing towards your cycling goals. Remember, proper recovery isn’t just about healing—it’s about returning stronger and more resilient.