Off-Season Training for Ultra-Cyclists: Unleashing Advanced Techniques
For ultra-cyclists aiming for peak performance, the off-season presents an invaluable opportunity for growth and improvement. It’s the perfect time to focus on advanced training techniques that can break through performance plateaus and enhance endurance. Off-season training for ultra-cyclists isn’t just about maintaining fitness; it’s about building a solid foundation for the upcoming season. Understanding and integrating specialized endurance training, cycling performance metrics, and mental conditioning are crucial for success.

Building Endurance with Interval Training for Ultra-Cyclists
Interval training is a cornerstone of endurance building for ultra-cyclists. This technique involves alternating periods of high-intensity work with lower-intensity recovery. It’s an efficient way to improve both aerobic and anaerobic capacities.
Implementing HIIT for Cyclists
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is particularly beneficial. A typical session may include short bursts of intense cycling followed by brief recovery phases. HIIT not only boosts endurance but also enhances VO2 max, allowing the heart and lungs to deliver more oxygen to muscles. To implement HIIT:
– Begin with shorter intervals of intense cycling.
– Gradually increase the duration and intensity.
– Ensure proper rest periods to maximize recovery.
Power-Based Training for Ultra-Cycling
Power-based training allows cyclists to train at the correct intensity. Power meters provide data on wattage output, which can guide targeted workouts. By focusing on power output, cyclists can work on specific muscle groups and energy systems to improve performance. A typical session involves:
– Performing sprints at or above a specific wattage target.
– Maintaining consistency over a set number of repeats.
– Tracking improvement over time for efficacy.
Understanding Cycling Performance Metrics
Grasping cycling performance metrics can significantly impact an ultra-cyclist’s success. Knowing how to use metrics like cycling cadence, VO2 max, and watts per kilogram (W/kg) is essential.
Cycling Cadence and Its Importance
Cycling cadence refers to the number of revolutions per minute (RPM) of the pedals. A higher cadence typically means improved endurance and less muscle fatigue. For ultra-cyclists:
– Maintain a cadence of 80-100 RPM for optimal endurance.
– Practice cadence drills during training sessions.
– Use a cadence sensor to monitor progress.
Improving VO2 Max
VO2 max measures the maximum volume of oxygen the body can use. Increasing this capacity is crucial for long-distance cycling:
– Incorporate long, steady rides at a moderate intensity.
– Use interval training to push higher heart rates.
– Train consistently to see long-term improvements.
Mental Resilience and Motivation Techniques
Physical prowess is only part of the equation; mental conditioning is equally important for ultra-cyclists. Techniques like mindfulness and visualization are essential tools for mental resilience.
Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness helps cyclists stay present and focused during long races:
– Practice mindfulness meditation regularly.
– Use breath control techniques to improve focus.
– Develop a routine to center yourself before races.
Visualization Exercises
Visualization helps in preparing mentally for various race scenarios:
– Imagine successful race outcomes regularly.
– Visualize challenging parts of a course.
– Use visualization to mentally rehearse race strategies.
Overcoming Race-day Anxiety
Race-day anxiety is common but manageable:
– Prepare thoroughly to boost confidence.
– Focus on the process, not just the outcome.
– Implement a pre-race routine to help reduce stress.
Data and Metrics for Effective Cycling
Using data and metrics can significantly enhance training effectiveness. Various tools and technologies can provide insights into a cyclist’s performance.
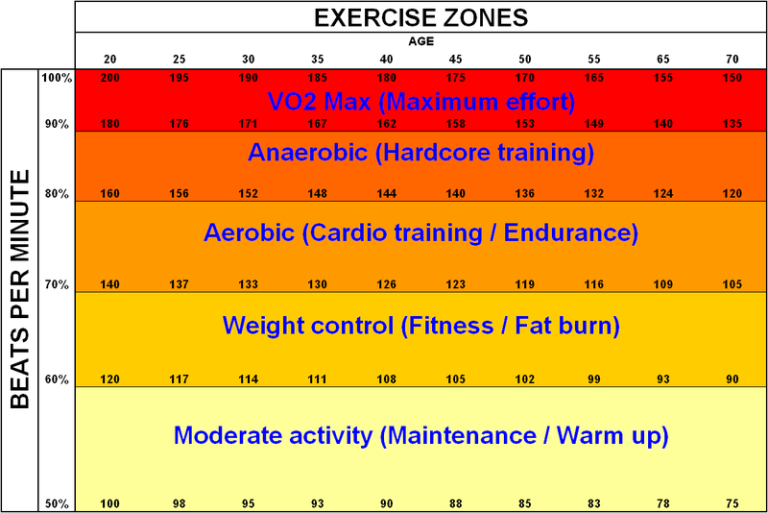
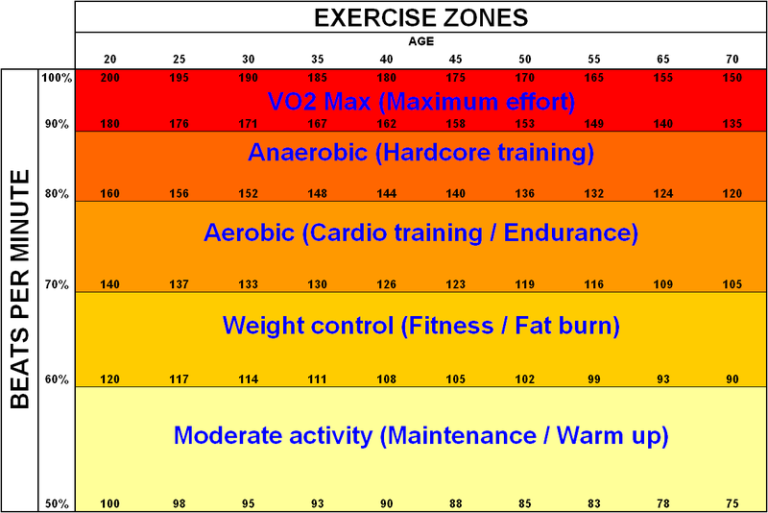
Heart Rate Zones
Understanding heart rate zones helps in creating structured workouts. Cyclists can track their heart rate to ensure they train effectively:
– Zone 1: Active Recovery
– Zone 2: Endurance Building
– Zone 3: Tempo
– Zone 4: Threshold
– Zone 5: VO2 Max Improvements
These zones help ensure that each session is productive and aligned with training goals.

Structured Workouts and Periodization
Periodization involves breaking training into cycles focusing on different skills. Structured workouts follow these phases to enhance performance:
– Base Mileage: Builds a strong aerobic foundation.
– Build Phase: Increases intensity and duration.
– Peak Phase: Focuses on race-specific skills.
– Recovery: Allows for rest and rejuvenation.
Advanced Training Techniques for Ultra-Cyclists
As you develop your off-season training routine, integrating advanced techniques can be a game-changer.
Core Stability and Strength Training
Core stability is vital for maintaining endurance over long distances:
– Include exercises like planks and Russian twists.
– Use resistance bands or weights for added difficulty.
– Ensure a balanced strength training program for overall muscle improvement.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Flexibility prevents injury and enhances overall riding comfort. Incorporate:
– Daily stretches focusing on key muscle groups.
– Yoga or Pilates sessions to improve flexibility and balance.
Nutrition Planning and Hydration Strategies
Nutrition is vital for performance and recovery:
– Plan balanced meals emphasizing protein, carbs, and healthy fats.
– Stay hydrated with tailored hydration strategies.
– Consider altitude training nutrition adjustments.
Altogether: Towards a Personalized Ultra-Cycling Approach
Every cyclist is unique, and a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. Choosing personalized coaching and focusing on individual training needs can result in excellent progress:
– Use performance analysis software to track improvements.
– Engage with a coach who understands your goals.
– Adapt training based on personal feedback and results.
FAQs
Q1: How does interval training benefit ultra-cyclists?
A1: Interval training enhances both aerobic and anaerobic capacities, improving endurance and efficiency in long-distance rides.
Q2: Why is mental conditioning important in ultra-cycling?
A2: Mental conditioning fosters resilience and focus, which are crucial for handling the psychological demands during long races.
Q3: What metrics should ultra-cyclists track regularly?
A3: Cyclists should focus on metrics like heart rate, power output, cadence, VO2 max, and lactate threshold to optimize their training.
Q4: How can flexibility exercises help ultra-cyclists?
A4: Flexibility exercises improve range of motion, reduce injury risk, and enhance comfort during long rides.
Q5: What role does nutrition play in off-season training?
A5: Proper nutrition supports performance, recovery, and overall health, enabling cyclists to train effectively and sustain energy levels.
Conclusion
Incorporating advanced training techniques during the off-season is crucial for ultra-cyclists aiming to elevate their performance. From endurance building with interval training to harnessing the power of data and mental conditioning, every aspect plays a pivotal role in success. Experiment with these techniques, adapt to personal needs, and embrace a strategic approach to training. Embark on this journey of self-improvement and share your experiences as you push towards your ultra-cycling goals.